Natural gas was created millions of years ago. Millions of years ago, the earth was filled with small sea creatures. Once they died their corpses fell to the bottom of the ocean. After many years, rock and sediment formed over the dead organisms and the pressure resulted in the creation of a substance called peat. The heat from the center of the earth caused the peat to turn into petroleum.
Natural gas is a fossil fuel which is primarily composed of methane (CH4). It has several various uses, such as being used to power industrial machinery, homes, and businesses. When compressed to less than 1 percent of its original value, natural gas can be used as a substitute for gasoline in cars.

In a typical operation of extracting natural gas, the excavation point is drilled, a concrete and metal casing is installed into the whole, and then a collection pump is installed above it. Natural gas is usually a by-product of processing oil. It can be found in coal beds, natural gas fields, and oil fields. Natural gas is extracted from gas wells thousands of feet deep. Since natural gas isn’t a pure product, it must first undergo processing before it can actually be used as a consumer fuel. The gas is then cleaned, processed, and sent to stations to be compressed. The additional elements, such as acid and mercury, are removed to make it usable by the consumer. After being compressed, it is put into pipe lines and sent to where it is needed. The decompression process of which gas is extracted from a field is referred to as retrograde condensation.
In more detail, raw natural gas is composed primarily of methane; although, it also contains a large number of other various hydrocarbon gases. The first stage in the process is to remove acid gases utilising amine or membrane treatment. The excess acid is typically processed into sulphur products. Secondly, any remaining water is removed, which is followed by the removal of mercury. Lastly, the nitrogen and natural gas liquids are removed from the natural gas by using extremely low temperatures (cryogenic distillation, which is created by the expansion of one or more elevated pressure process streams). The final result is the natural gas that our modern world utilises for several purposes.
In a summarized process, here are the steps below:
Step 1: Firstly, the acid must be removed from the gas. This can be achieved by an amine treating and a sulfinol process which causes the acid to be separated from the gas.
Step 2: Secondly, the natural gas must be dehydrated, stripping it of moisture. It goes through a glycol and PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) unit, ridding it off excess moisture. An adsorption process is one which accumulates the atoms and molecules on the surface of a material.
Step 3: In addition, mercury must be removed from the gas. Once the natural gas is dehydrated with the process mentioned in the previous step, the mercury can be removed with activated carbon. Activated carbon is extremely porous (possesses a large amount of void) and can be used for adsorption and chemical reactions.
Step 4: Then, nitrogen must be removed from the gas. Simply put, an adsorption process removes the nitrogen.
Step 5: Finally, the natural gas can be distributed and be utilised by consumers. It can be used in various processes such as residential use, power generation, cooking, powering natural-gas vehicles, fertilization, and aviation.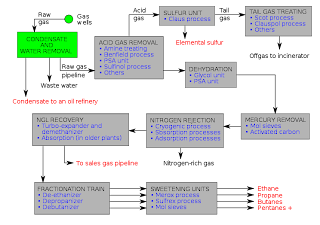
Top gas producers around the world
1. Russia … 656.2 billion cubic meters (19.9% of estimated world total)
2. United States … 490.8 billion cubic meters (14.9%)
3. Canada … 178.2 billion cubic meters (5.4%)
4. Iran … 101 billion cubic meters (3.1%)
5. Algeria … 84.4 billion cubic meters (2.6%)
6. United Kingdom … 84.2 billion cubic meters (2.6%)
7. Norway … 83.4 billion cubic meters (2.5%)
8. Netherlands … 77.3 billion cubic meters (2.3%)
9. Indonesia … 74 billion cubic meters (2.2%)
10. Turkmenistan … 72.3 billion cubic meters (2.2%)

Natural Gas has a variety of advantages, each with a unique ability to add to the overall value of using Natural Gas.
Using Natural Gas is great for YOU because:
- It is very inexpensive compared to all the other sources of energy and will save you a lot of money
- It is one of the world's safest sources of energy
- You will never run out of fuel because it is connected to an underground pipeline
- It requires almost no maintenance or repairs
- It does not smell like other sources of energy
Using Natural Gas is great for the ENVIRONMENT because:
- It burns cleanly compared to coal, and oil
- There is 70% less carbon dioxide compared to other fossil fuels
- It helps improve the quality of air and water
- It does not produce ashes after its energy release
- It is natural unlike other sources of energy
You can even use this source of energy in a variety of places:
- You can use it outside for your barbecue, pool heater, and gas lights
- In the basement for your water heater and clothes dryer
- in the kitchen for cook top
- in the den and living room for your natural gas fireplace.
Disadvantages
Considering Natural Gas is one the most popular sources of energy in the world, there are not many disadvantages, but there are a few.
1. Natural Gas is fairly combustible and methane explosions are possible.
2. It is a Non-Renewable resource
3. It is very toxic if its inhaled in large amounts
4. It also creates cavities in the earth from pressure exerted by the gas.
5. Even though it pollutes one of the least amounts out of the energy sources, it still pollutes a little and that is a disadvantage.
There are many uses for natural gas. Although it’s main use is for heat it can be used for a range of different things. They are used in homes for gas appliances such as gas powered ovens, gas heated dyers and furnaces. They are also widely used in transport such as cars, trains, buses and airplanes. Natural gas can also be used to manufacture a variety of products such as fabrics, glass, steel, plastics and paint.

Natural gas, which is primarily methane, fuels a vehicle in a process which is very similar to that of gasoline powered vehicles; the concepts of internal combustion between the two are virtually identical. In cars, the natural gas is burnt and the combustion of the gas acts as the energy process. In a combustion engine, the fuel is mixed with air, which is pumped into a small space, referred to as the combustion chamber. The sparkplug initiates an electric jolt which causes the mixture to burn in an explosive reaction, referred to as oxidation. Then, the pressure created from the combustion of the fuel/air mix in the chamber drives a piston; which is correlated through a series of gears and shafts to the wheels and axels.
References
The Need project. (2004). Natural gas. Retrieved from http://www.mms.gov/omm/pacific/kids/Watts/Appendix/91.%20NGas.pdf
CIA World Factbook. (2008, April 25). Top natural gas countries. Retrieved from http://internationaltradecommodities.suite101.com/article.cfm/top_natural_gas_countries
The Greening Earth Society , . (2000, February 19). About Natural gas. Retrieved from http://www.bydesign.com/fossilfuels/Links/html/natural_gas.html
Richard Thomas, . (2009). How Is Natural Gas Extracted, Processed & Refined?. Retrieved from http://www.ehow.com/how-does_4900022_natural-gas-extracted-processed-refined.html
Secondary Energy Info book, . (2008). Natural Gas. Retrieved from http://www.need.org/needpdf/infobook_activities/SecInfo/NGasS.pdf
Sidney. How is Natural gas Produced. Retrieved from http://www.ehow.com/how_4686639_natural-gas-produced.html
Nicholson, J. How does Natural gas power a vehicle?. Retrieved from http://www.ehow.com/how-does_4576755_natural-gas-power-vehicle.html
Techfaq. What are Natural gas cars?. Retrieved from http://www.tech-faq.com/natural-gas-cars.shtml
Perles, C. How a Compressed natural gas system works. Retrieved from http://www.ehow.com/how-does_4898641_compressed-natural-gas-system-works.html
Wikipedia, . (2009, 08 29). Natural gas processing. Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_gas_processing
Drake, A. (2005). Natural gas. Retrieved from http://naturalgasw.a.tripod.com/index.html
Advantages and disadvantages of energy sources. Retrieved from http://www.spsu.edu/tmgt/vasa-sideris/MGNT4125/ADVANTAGES_AND_DISADVANTAGES_OF_ENERGY_SOURCES.htm
Tounzen, S. Natural gas advantages and disadvantages. Retrieved from http://www.ehow.com/about_4761044_natural-gas-advantages-disadvantages.html